What is Injection Molding? (And how does it compare to other processes?)
Injection Molding in Mexico
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing gaskets and seals by injecting pre-heated material into a mold using a screw and piston injection unit. Injection presses offer significantly more control over all process parameters, including the material’s temperatures at various points in the process and the speed and volume of the material introduced into the mold. It is a more advanced iteration of transfer molding, utilizing special equipment, and offers unique benefits, especially for those looking to produce a high volume of complex precision parts.
Diagram: Open Injection Mold
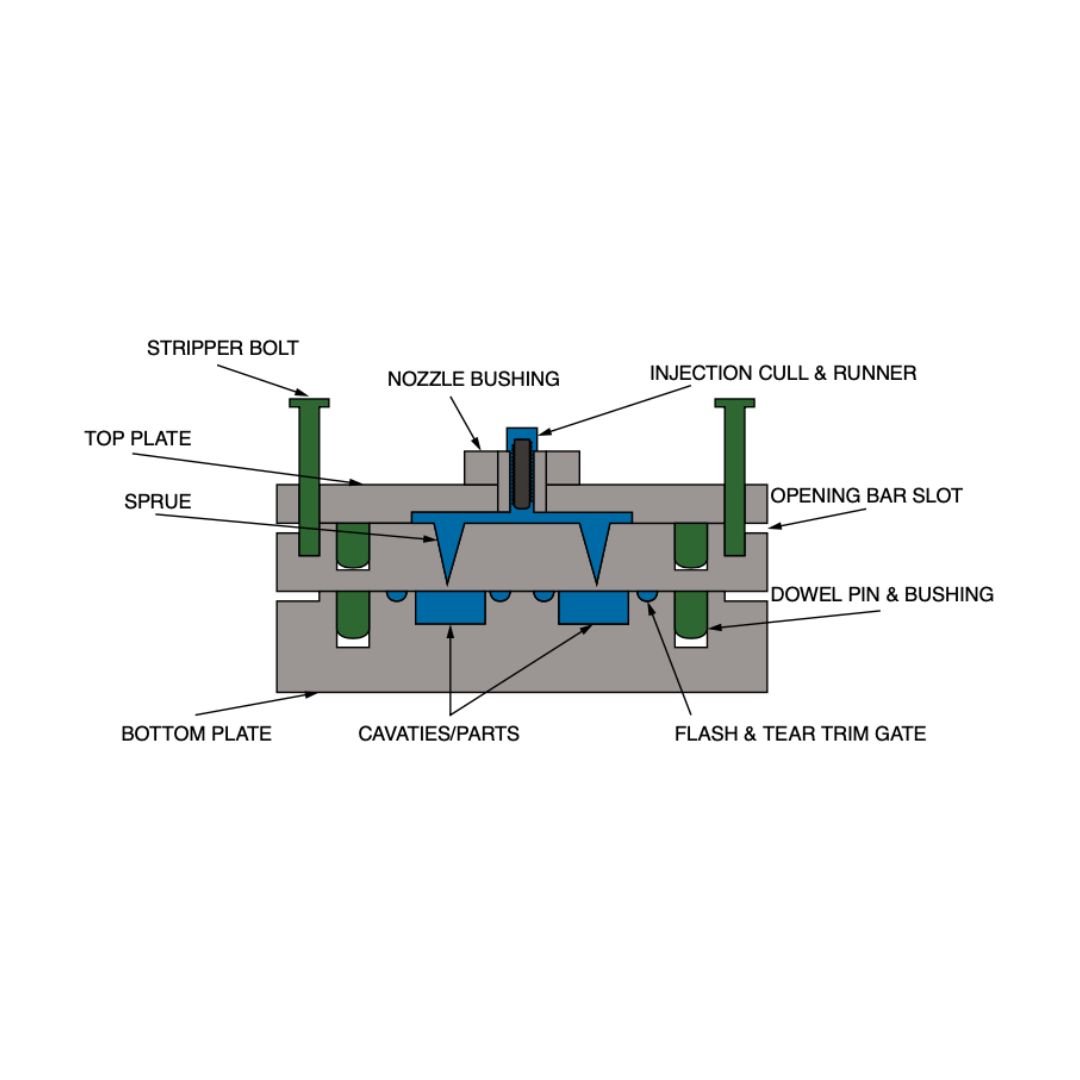
Diagram: Filled Injection Mold
Injection molding is one of the most popular processes for achieving high-quality and cost-effective parts. As stated previously, parts are produced by injecting material into a mold.
Step 1: A rotating extruder screw automatically feeds a ribbon of raw material into a heated barrel where the rubber is pre-heated to the optimum temperature. With silicone rubber, a secondary ram known as a “stuffer” introduces a bulk quantity of material into the injection unit.
Step 2: A hydraulic piston injects the pre-heated and masticated material into a hot mold cavity.
Step 3: Now, inside the mold cavity, the material cures quickly due to the heat produced while quickly entering the cavity, combined with the mold temperature and pressure.
Benefits of Using Injection Molding
The popularity of injection molding is due, in part, to several unique advantages, which include:
High Precision
Injection molding can achieve more complex and tighter tolerance geometries than other molding methods. This is because an injection press forces heated, and therefore less viscous, raw material into a mold under high pressure.
Material handling also plays an integral part in improving product precision. Instead of an operator handling the material, the charging of the injection barrel by the rotating screw is automated, and therefore, the volume of the injected material is exact. Material feed automation also contributes to more consistent cycle times with reduced shot-to-shot size variation.
Repeatability
When performed by experts, the injection molding process is highly controlled and repeatable. Once a part is successfully produced, the following parts will be nearly identical to the original. And because injection molding is a more automated process, there is no manual handling of materials or molds, removing many of the process variables caused by press operators.
Moreover, the faster cycle times for injection molding means that the molding tool spends less time open. Keeping the tool closed creates a more stable heat profile within the tool and results in better cycle-to-cycle consistency.
Diagram: Injection Molding Equipment
Minimal Material Waste
Some forms of injection molding can further reduce material waste by employing a “cold runner” system. In basic injection molding, the rubber is introduced through
a central injection point in the middle of the tool and fed through a gallery of hot runners to various points of the part geometry. Depending upon the complexity and size of the part, this can lead to a significant amount of waste rubber in these cured runners.
One way to mitigate this waste is by using a “cold runner” system where a cooled manifold splits the central flow of material into multiple streams kept at a temperature below the cure point. These multiple streams can then feed the raw material into several points in the part cavity, significantly reducing or, in some cases eliminating the waste of cured sprues. To further advance a cold runner system, valve gates systems can introduce the raw material directly into the part cavity and then shut off the rubber flow through a pintle valve.
These methods reduce material costs but also increase the complexity and cost of the tooling. So a valve-gated cold runner system is primarily considered for high-volume programs where the material cost savings justify the substantial tooling investment.
To learn more about Injection Molding and other processes like compression transfer molding, download our free White Paper and watch our 2-minute video.
2-minute video: Injection Molding in Mexico